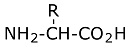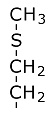|
|
Amino Acid: 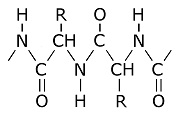
The carboxyl group is the usual organic acid. Acid means that the hydrogen has a tendency to separate becoming plus charged while leaving a minus charge on the oxygen. There are 20 amino acids. They each have a different R group. Here are three examples of R groups:
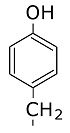
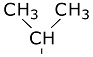
Methionine: Tyrosine: Valine: The chains fold over each other while being synthesized creating a three dimensional structure which is globular. Tertiary Structure - is the over-all structure.Secondary Structure - is the interaction between segments which are near each other.Primary structure - is the sequence of subunits in the chain.Secondary structure includes hydrogen bonds. These bonds are very weak individually, but they tend to be numerous. A hydrogen bond means that a hydrogen atom attached to one group is drawn to a negative charge on another group near it. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||