 |
|
Research Photo Pages
|
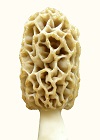
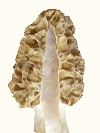
Glossary Agar. A gel from seaweed extract which is resistant to microbial attack. Agar Slants. Culture tubes with agar solidified almost horizontally for long surface. Alleles. Minor variations of the same gene. Allotypes. Small or concealed variations of a type. Amino Acids. The building blocks of proteins. Ascocarp. A large structure for producing ascospores. (the mushroom) Ascospores. Spores within an ascus (sack). ATP. A molecule which carries useable energy through all types of cells. Autolysis. Self-disintegration of yeasts or bacteria to recycle nutrients by breaking down proteins to amino acids and genetic material to nucleosides. Conidia. External spores of molds on stalks one cell in width. Deliquescence. The disintegration of mushroom tissue. Differentiation. Change in cellular or multicellular form. Complex but not simple change. Endotrophic. Endo (within). Troph (nutrition). Occurring in absence of exogenous (external) nutrients. Endotoxin. Toxin in the cell walls of all Gram-negative bacteria. Eukaryotic. Higher cells with membranes and complexity. Extracellular. Outside the cell. Genotype. Genetic makeup. Glycolysis. An enzyme path for breaking down sugars. Gram-positive or negative. Two major cell wall types dichotomizing all bacteria. Heterokaryosis. Multiple types of nuclei within cells. Induction. The first critical step in initiating differentiation. Isolation. A procedure for separating a species from contaminating species in pure cultures. Morchella. Genus name for morel mushrooms. Morphology. Overall form. Mycelium. The aggregate of long, single-cell-wide, filaments (hyphae) of fungi. Nucleic Acids. The building blocks of genetic material. Petri Plates. Glass dishes with a lid to maintain sterile agar or pure cultures. pH. Acidity or alkalinity. 7.0 is neutral. Lower is acid. Phenotype. Outward appearance, assuming controlled result. Physiology. Integrated functioning of all chemical processes in a cell. Prokaryotic. Lower cells without membranes or complexity. (bacteria) Protons. Hydrogen ions, plus charged. They create acidity. Pure Culture. A single species with no contaminating species in the culture vessel. Rhizosphere. A zone of biological activity around roots. Sclerotia. An outgrowth of cells used by Morchella as the equivalent of
underground spores.
|
